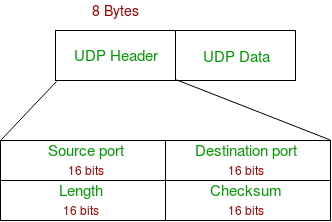
UDP报文最大长度

UDP
由于udp报文头中使用16bits表示长度,因此最大长度是2的......


UDP
由于udp报文头中使用16bits表示长度,因此最大长度是2的......
class Solution {
public:
int minDistance(string word1, string word2) {
int m = word1.size(),n = word2.size();
int l = lcs(word1,word2,m,n);
return m + n -2 * l;
}
private:
int lcs(string word1,string word2,int m,int n) {
if(m == 0 || n == 0) return 0;
if(word1[m - 1] == word2[n - 1]) {
return 1 + l......
贪心算法,从最后向前填充构造字典序列最小值,字符串初始为n个'a',这样在保证了字符串长度,如果不预先从k中减去n个a,那么在我们计算过程中,有可能会生成小于n个字符的结果,处理起来比较麻烦。
class Solution {
public:
//计算生成字典序最小字符串,贪心算法,从后面开始先使用最大z
string getSmallestString(int n, int k) {
string res(n,'a');
k -= n;
int i = n - 1;
while(k > 0) {
int fill = min(k,25);
k -= 25;
re......
LRU题目姊妹篇,个人认为这道题难度比LRU大,主要需要记录访问次数,如果访问次数一致再按照LRU访问时间。解题思路参考了力扣官方文章
C++里可以使用set(底层红黑树),排序依据是访问次数和访问时间,因此需要重载比较运算符。
方法一AC代码:
struct Node {
int m_cnt, m_time, m_key, m_value;
Node(int cnt, int time, int key, int value):m_cnt(cnt), m_time(time), m_key(key), m_value(value){}
bool operator < (co......
实现LRU,巧合的是工作当中有实际使用该算法。
class LRUCache {
public:
LRUCache(int capacity) :m_capacity(capacity) {}
int get(int key) {
auto it = cache.find(key);
if(it == cache.end())
return -1;
visited(it);
return it->second.first;
}
void put(int key, int value) {
auto it = cache.find(key);
if(it != cache.end......
暴力破解与最直观的写法:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public......
首先贴出来第一遍写的AC代码,目的就是为了AC,后面从可读性、性能等方面优化。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };......
这道题目,个人认为非常经典,虽然看到题目要求计算不同BST个数,一般会联想到动态规划,但动态规划如何求解递推方程成为了最大的难点。
在之前的题目中我们解决了台阶问题,递推方程相对简单:
定义f(n)表示走到第n台阶可能的走法(每次可以走一个台阶或者两个台阶),那么递推方程:
f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-2)表示走到第n台阶走法等于走到第n-1台阶的走法加上走到n-2台阶的走法。
而96这道题相对没有那么好写递推公式。
显而易见对这道题目而言DP[n]表示数字n对应不同BST数目,dp[0]=dp[1]=1
dp[2]推导方法为:1 2都可以为根节点:
当1为根节点时左子树为D......
BRUTE FORCE暴力破解方法如下:
class Solution {
public:
int maxArea(vector<int>& height) {
//BRUTE FORCE
int res = 0;
int size = height.size();
for(int i = 0;i<size;i++)
{
for(int j=i+1;j<size;j++)
{
res = max(res,(j - i) * min(height[i],height[j]));
}
}
return res;
}
};
不出意料的Time Limit......
动态规划解法,这里的dp[i][j]表示word1[0----i]变化到word2[0----j]所需要的最小操作步骤。
class Solution {
public:
int minDistance(string word1, string word2) {
int m = word1.size(),n = word2.size();
vector<vector<int>> dp(m+1,vector<int>(n + 1,0));
for(int i = 0;i <= m;i++) dp[i][0] = i;
for(int j = 0;j......