本文参考Unix linux编程实践教程,完成编写pwd命令,并介绍相关核心知识点。
命令pwd用来显示到达当前目录的路径。例如:
root@ubuntu:~/uup/experiments# pwd
/root/uup/experiments
root@ubuntu:~/uup/experiments#
pwd命令的实现思路:
1.得到当前目录.的i节点号
2.然后改变当前目录为父目录
3.与查询出来的目录信息通过i节点号比较
4.重复此过程
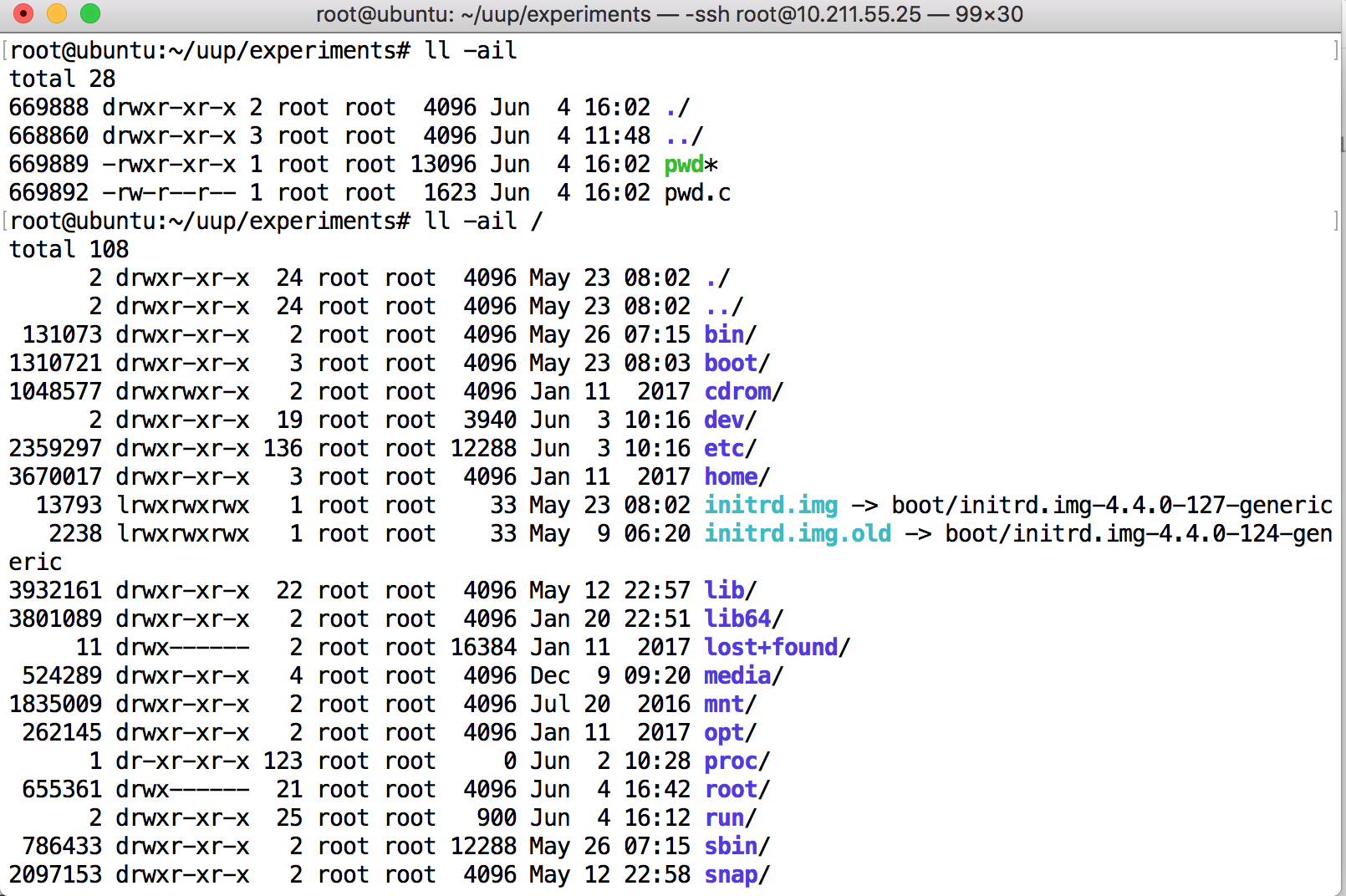
由于在根目录. 和..的i节点号相同,因此递归终止的条件是到达根目录。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <inttypes.h>
ino_t get_inode(char*);
void printpathto(ino_t);
void inum_to_name(ino_t,char*,int);
int main()
{
printpathto(get_inode(".")); //print path to here
putchar('\n');
return 0;
}
void printpathto(ino_t this_inode)
{
ino_t my_inode;
char its_name[BUFSIZ];
/*如果本目录的i-节点与上级目录不同,即本目录不是根目录root*/
if (get_inode("..") != this_inode)
{
chdir(".."); //进入上级目录
inum_to_name(this_inode,its_name,BUFSIZ);
my_inode = get_inode(".");
printpathto(my_inode);
printf("/%s",its_name);
}
}
void inum_to_name(ino_t inode_to_find,char* namebuf,int buflen)
{
DIR* dir_ptr;
struct dirent* direntp;
dir_ptr = opendir(".");
if (dir_ptr == NULL)
{
perror(".");
exit(1);
}
while((direntp = readdir(dir_ptr)) != NULL)
{
if(direntp->d_ino == inode_to_find)
{
strncpy(namebuf,direntp->d_name,buflen);
namebuf[buflen-1] = '\0';
closedir( dir_ptr);
return;
}
}
fprintf( stderr , "error looking for inum %ju\n" ,(uintmax_t)inode_to_find);
exit (1) ;
}
ino_t get_inode(char* fname) //根据文件名,返回inode number
{
struct stat info;
if (stat(fname, &info) == -1)
{
fprintf( stderr , "Cannot stat ");
perror(fname);
exit (1);
}
return info.st_ino;
}
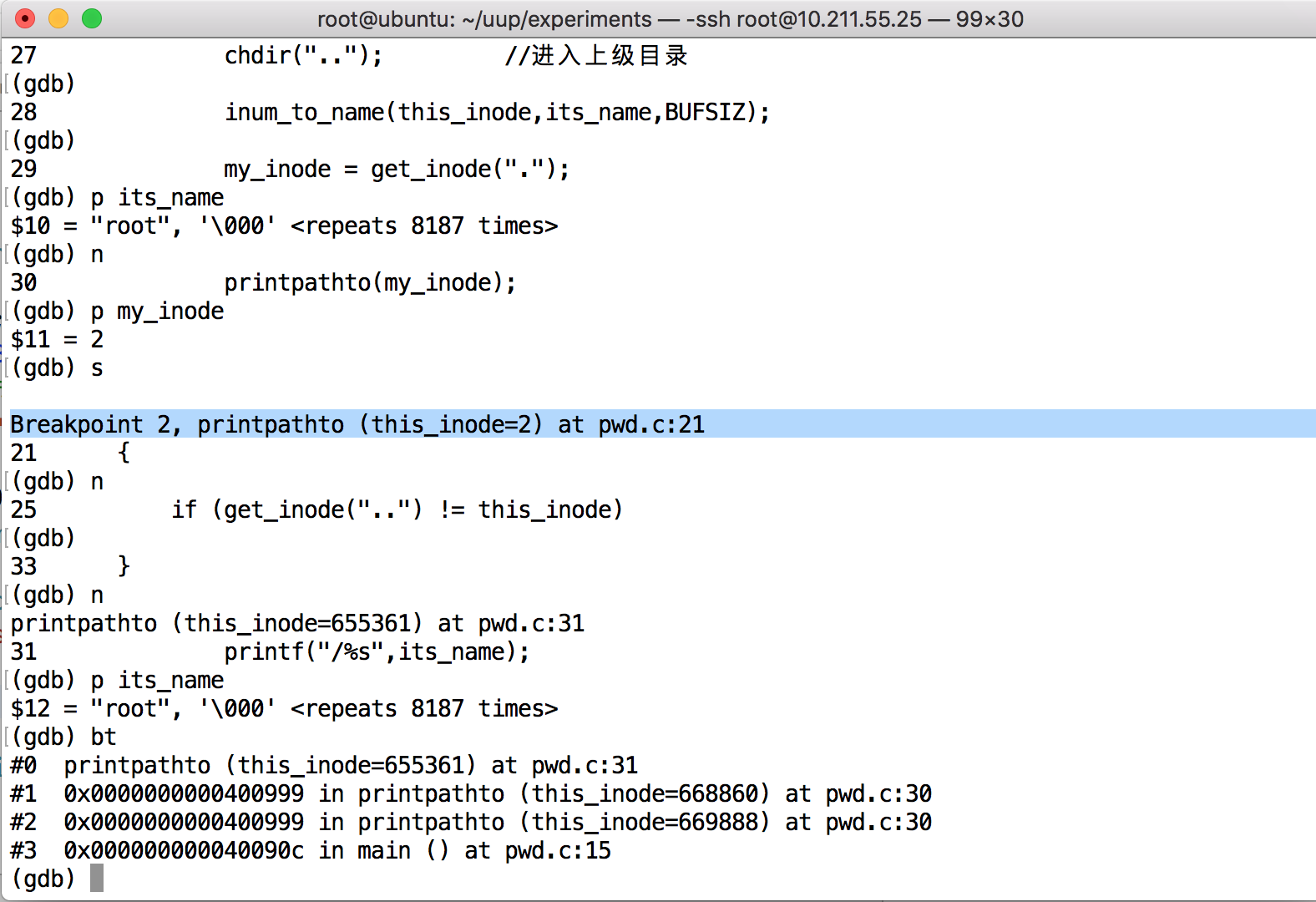
可以通过使用gdb调试来理解上面的代码:
验证..和.只有在根目录才相同: