终端驱动程序的模式
以一个简短的例子作为开始:
/* rotate.c : map a->b, b->c, .. z->a
* purpose: useful for showing tty modes
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
int main()
{
int c;
while ( ( c=getchar() ) != EOF ){
if ( c == 'z' )
c = 'a';
else if (islower(c))
c++;
putchar(c);
}
}
总结:
1.假如我们在敲回车前输入abx然后删除x,程序中未得到输入的字符x
2.敲击键盘的同时字符显示在屏幕上,但是直到按了回车键,程序才收到输入;
3.Ctrl+C键结束输入并终止程序
上述程序不做这些操作,缓冲、回显、编辑和控制处理都由驱动程序完成。
缓冲和编辑包含规范处理,此时终端连接处于规范模式。
非规范模式
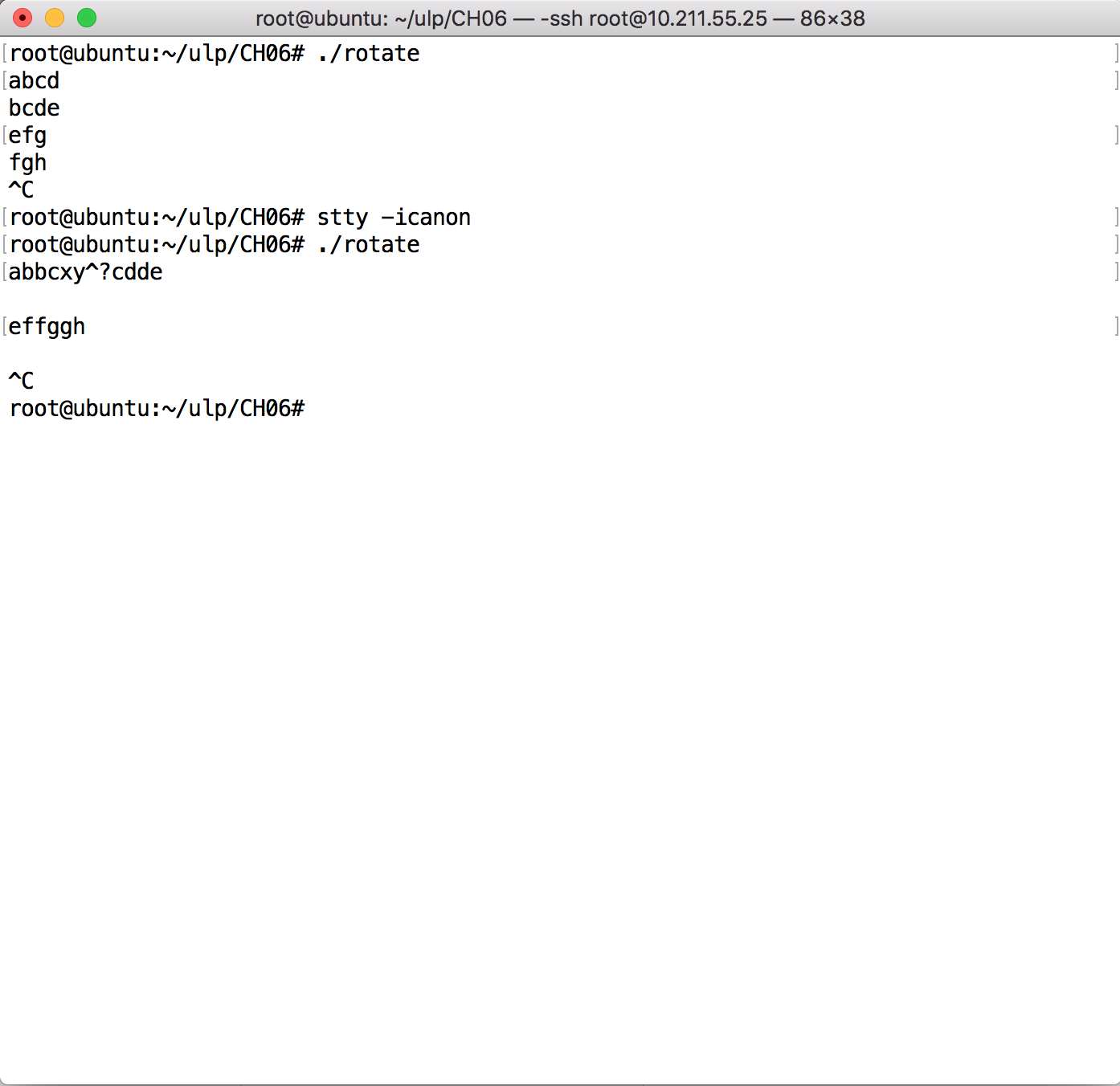
命令stty -icanon关闭了驱动程序中的规范模式处理,由于非规范模式中没有缓冲,输入字符'a'直接输出处理结果'b'。用户输入未被缓冲可能是一件麻烦事。当用户试图删除一个字符,驱动程序不能做任何事情,字符早就传送给程序了。
下面演示处于规范模式与非规范模式下执行情况,输入均为:abx(删除x)cd efg(Ctrl +C)
编写play_again程序
很多应用程序,例如自动取款机和计算机游戏,都会向用户提出yes/no的问题。下面是程序最终的源代码:
/* play_again4.c
* purpose: ask if user wants another transaction
* method: set tty into chr-by-chr, no-echo mode
* set tty into no-delay mode
* read char, return result
* resets terminal modes on SIGINT, ignores SIGQUIT
* returns: 0=>yes, 1=>no, 2=>timeout
* better: reset terminal mode on Interrupt
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#define ASK "Do you want another transaction"
#define TRIES 3 /* max tries */
#define SLEEPTIME 2 /* time per try */
#define BEEP putchar('\a') /* alert user */
/*
* skip over non-legal chars and return y,Y,n,N or EOF
*/
char get_ok_char()
{
int c;
while( ( c = getchar() ) != EOF && strchr("yYnN",c) == NULL )
;
return c;
}
int get_response( char *question , int maxtries)
/*
* purpose: ask a question and wait for a y/n answer or timeout
* method: use getchar and complain about non-y/n input
* returns: 0=>yes, 1=>no
*/
{
int input;
printf("%s (y/n)?", question); /* ask */
fflush(stdout); /* force output */
while ( 1 ){
sleep(SLEEPTIME); /* wait a bit */
input = tolower(get_ok_char()); /* get next chr */
if ( input == 'y' )
return 0;
if ( input == 'n' )
return 1;
if ( maxtries-- == 0 ) /* outatime? */
return 2; /* sayso */
BEEP;
}
}
void set_cr_noecho_mode()
/*
* purpose: put file descriptor 0 into chr-by-chr mode and noecho mode
* method: use bits in termios
*/
{
struct termios ttystate;
tcgetattr( 0, &ttystate); /* read curr. setting */
ttystate.c_lflag &= ~ICANON; /* no buffering */
ttystate.c_lflag &= ~ECHO; /* no echo either */
ttystate.c_cc[VMIN] = 1; /* get 1 char at a time */
tcsetattr( 0 , TCSANOW, &ttystate); /* install settings */
}
void set_nodelay_mode()
/*
* purpose: put file descriptor 0 into no-delay mode
* method: use fcntl to set bits
* notes: tcsetattr() will do something similar, but it is complicated
*/
{
int termflags;
termflags = fcntl(0, F_GETFL); /* read curr. settings */
termflags |= O_NONBLOCK; /* flip on nodelay bit */
fcntl(0, F_SETFL, termflags); /* and install 'em */
}
/* how == 0 => save current mode, how == 1 => restore mode */
/* this version handles termios and fcntl flags */
void tty_mode(int how)
{
static struct termios original_mode;
static int original_flags;
static int stored = 0;
if ( how == 0 ){
tcgetattr(0, &original_mode);
original_flags = fcntl(0, F_GETFL);
stored = 1;
}
else if ( stored ) {
tcsetattr(0, TCSANOW, &original_mode);
fcntl( 0, F_SETFL, original_flags);
}
}
void ctrl_c_handler(int signum)
/*
* purpose: called if SIGINT is detected
* action: reset tty and scram
*/
{
tty_mode(1);
exit(2);
}
int main()
{
int response;
void ctrl_c_handler(int);
tty_mode(0); /* save current mode */
set_cr_noecho_mode(); /* set -icanon, -echo */
set_nodelay_mode(); /* noinput => EOF */
signal( SIGINT, ctrl_c_handler ); /* handle INT */
signal( SIGQUIT, SIG_IGN ); /* ignore QUIT signals */
response = get_response(ASK, TRIES); /* get some answer */
tty_mode(1); /* reset orig mode */
return response;
}
在上面代码中我们捕获SIGINT,重置驱动程序,然后返回。